The Future of Quality Engineering: 6 Key Impacts of Technology
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Converging Technology
The intersection of various technologies presents unique opportunities. Just as lighting revolutionized distribution networks and gasoline-powered vehicles thrived due to extensive supply chains, electric vehicles face a similar challenge. Autonomous vehicles, too, rely on a synergy of artificial intelligence, sensors, and robust connectivity to ensure security and privacy, among other essential factors.
The blend of technologies within a global economy is crucial for rapid advancement. Only those who can swiftly adapt will thrive. This article outlines six effects of converging technologies on Quality Engineering, beginning with an overview of the innovation landscape.
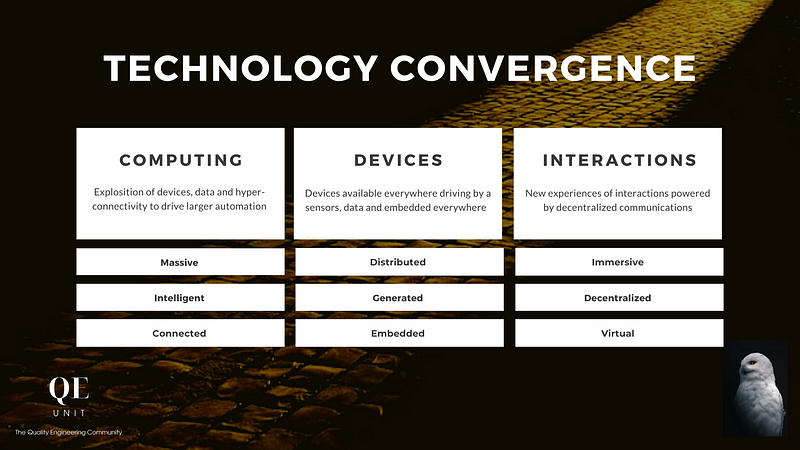
The Emerging Landscape of Converging Technology
Since the early 2000s, the rise of Cloud computing, Big Data, APIs, and the Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed our environment alongside social media and smart devices in everyday life. This technological surge has accelerated progress in three key areas: computing, devices, and interactions.
#### Massive, Intelligent, Connected Computing
Daily, we generate approximately 2.5 exabytes of data—a figure that continues to grow due to the proliferation of network access, user-generated content, and an increasing number of devices. To handle this vast data, several technologies are stepping up:
- Quantum Computing aims to tackle intricate problems across large datasets at speeds up to 100 million times faster than traditional methods.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is designed to automate complex decision-making processes more efficiently than human teams, both in Cloud environments and at the Edge.
- Connected Computing facilitates collaboration among humans and devices through advanced networks, including 5G, balloons, and satellites.
#### Distributed, Generated, Embedded Devices
The IoT, or Internet of Things, encompasses a network of connected devices equipped with sensors, processing capabilities, and communication tools. Projections suggest that the number of IoT devices will soar from 11 billion to 30 billion by 2025—outnumbering humans by a significant margin. This shift will dramatically alter both our personal and professional interactions:
- IoT and robotics will become integrated into most objects we use daily, driven by data processing.
- 3D Printing and material science will innovate the creation of new materials, reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Nanotechnology and Biotech will transform health and living systems by embedding technology within ecosystems.
#### Immersive, Decentralized, Virtual Interactions
These advancements in computing, devices, and materials pave the way for novel experiences. The boundaries between the physical and digital realms are expected to blur, increasing the demand for security and privacy. New capabilities in our daily lives will emerge through various lenses (often referred to as Web3):
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR, AR) will provide more immersive experiences, such as virtually visiting museums or engaging in location-based games like Pokémon GO.
- Virtual Worlds and Avatars will evolve from traditional blogs and chat rooms, enabling interactions in digital environments for work, play, and meetings (e.g., the “Metaverse”).
- Blockchain and Smart Contracts are rapidly expanding, driven by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, to decentralize assets and establish trust.
These innovations will influence every industry based on their unique dynamics, with Quality Engineering being particularly affected at the core of software development.
Chapter 2: Opportunities from Converging Technology in Quality Engineering
Quality Engineering embodies the discipline that ensures continuous value delivery throughout the software lifecycle, from initial digital concepts to operational execution. The convergence of these technologies is creating new experiences, increasing both complexity and criticality, which directly affects software practices from end to end.
To build a digital infrastructure with interconnected components, the optimization of two key flows is essential for ongoing value delivery:
- From Customer to Code, which translates ideas into actionable software requirements through Lean Design Thinking.
- From Code to Customer, which involves designing, delivering, and operating software that meets quality standards through Lean Software Factories.
Only the most agile players in this dynamic ecosystem will endure. By executing quicker iterations, an entity can learn, adapt, and enhance its value proposition more rapidly. Converging technologies are set to further accelerate these iterative cycles:
- Quantum computing, cloud solutions, and AI will enable more functions to be performed across expansive networks.
- An increasing number of devices and interactions will lead to greater data availability.
- Enhanced integration and collaboration among digital agents will create new opportunities.
Now, let's delve into how Quality Engineering can harness these converging technologies to enhance continuous value delivery.
Leveraging Converging Technology in Quality Engineering
The current software ecosystem faces performance challenges due to various limiting factors throughout the value chain, such as poor communication among teams, integration difficulties, and system complexities. Converging technologies will help streamline software operations.
We anticipate the following sequential opportunities:
- Foundations of Quality Engineering will be reinforced by more advanced computing, automation, and integration, simplifying deployment pipeline management, environments, and data handling.
- Accelerated Collaboration will be facilitated through enhanced interactions enabled by robust networks and automation in collaborative efforts.
- Automated Quality Requirements, including security and reliability, will leverage data, AI, and automation for tasks like conformance checking and monitoring.
- Enhanced Observability will arise from the large-scale processing of complex datasets, yielding insights into value streams and processes.
- Individual Productivity Gains driven by AI assistants will begin with specific coding and testing applications, leading to broader data correlations over time.
- Autonomous Systems will be capable of processing data significantly faster than human teams, automating tasks like test definition and monitoring based on requirements.
Like all transformations, these advancements will primarily be incremental, progressively replacing less valuable tasks for those equipped with the necessary foundations.
These converging forces are likely to inspire the development of:
- Quality Engineering Platforms with seamless integrations with primary products and hyper-automation featuring intelligent suggestions.
- Unified Development Environments that incorporate pipelines, testing gates, deployment mechanisms, and built-in observability across multi-cloud and edge infrastructures.
- Next-Generation Low-Code Solutions that mature to meet industrial requirements for scalability and portability over time.
The landscape of Quality Engineering is poised for significant change.
Chapter 3: Capturing Value Through Quality Engineering
Converging technologies are set to profoundly transform our digital environment in the coming years. Identifying potential scenarios is essential for effective planning. Organizations must adapt at an increasingly rapid pace. New ventures will capitalize on these technological capabilities, while existing entities must evolve quickly.
A continuous commitment to Quality Engineering will streamline the software value chain, ensuring quality at speed. The clock is ticking; as you deliberate, terabytes of data are being generated, ready to be harnessed by others.
Converging technology also impacts your organization. For more insights on Quality Engineering, follow the QE Unit for access to the free ebook “60 Practices For Quality Engineering,” exclusive community content, and weekly updates.
The first video titled "How is QA/QE done in tech companies? | Quality Engineering Meetup" discusses the approaches and methodologies utilized in Quality Engineering across various tech companies, shedding light on best practices and innovative strategies.
The second video, "Quality Engineering: The Future of Software Testing," explores the evolving landscape of software testing and how Quality Engineering will adapt to meet the challenges posed by new technologies.
References
Peter H. Diamantis, Steven Kotler, The Future Is Faster Than You Think: How Converging Technologies Are Transforming Business, Industries, and Our Lives. Simon & Schuster.
Mauro F. Guillen, 2030: How Today’s Biggest Trends Will Collide and Reshape the Future of Everything. St. Martin’s Press.
Marco Iansiti, Karim R. Lakhani, Competing in the Age of AI: Strategy and Leadership When Algorithms and Networks Run the World. Harvard Business Review Press.
Yves Caseau, The Lean Approach to Digital Transformation: From Customer to Code and from Code to Customer. Productivity Press.