Exploring Mind Reading: The Intersection of AI and Neuroscience
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Mind Reading
The journey of artificial intelligence began in the 1950s with the advent of the perceptron model, which was initially designed to classify images as “male” or “female.” Fast forward to today, AI has evolved to encompass various applications, including the intriguing concept of mind reading. But what exactly does this entail? What are its claims and scientific validity? Let’s delve deeper into this fascinating subject.
Mind reading refers to the popularized concept of Brain Decoding, which involves examining brain data to infer thoughts and experiences. Brain data typically indicates activation patterns occurring when the brain is engaged—essentially when an individual is thinking or performing a task. To fully grasp the intricacies of decoding, we must also consider its counterpart: encoding.
Encoding describes the transition from an external stimulus to the brain's activations. For instance, if the stimulus is visual—such as observing an object—your occipital lobe will exhibit activity. Within the realm of visual stimuli, distinct instances correspond to unique activation patterns. For example, viewing the word “cat” triggers different brain responses than seeing the word “dog.” This differentiation is crucial for word recognition; if both words elicited identical activation patterns, distinguishing between them would be impossible. Similarly, auditory stimuli activate the temporal lobe.
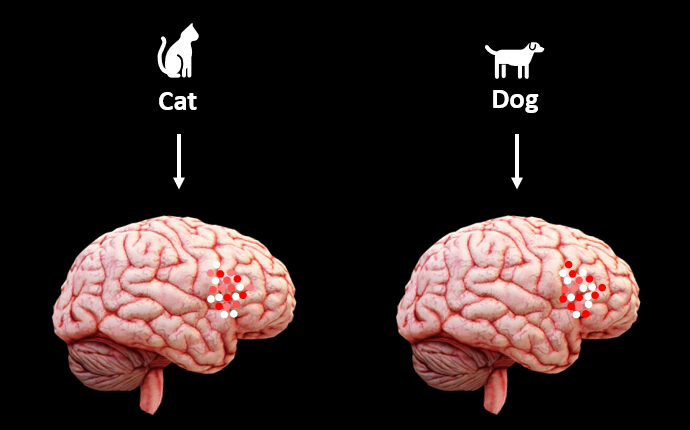
The brain's activation patterns vary based on the stimuli presented, even if they belong to the same category. In essence, the specific stimulus you encounter (alongside other complex factors like mood and multimodal integration) will activate different regions of the brain.
Encoding aims to elucidate how stimuli translate into brain activations, while decoding reverses this process: it seeks to interpret how brain activation patterns can reveal the underlying stimulus. In other words, it’s about deducing what a person is observing, listening to, or imagining by analyzing their brain activity.
Currently, this process lacks precision, as it relies heavily on inference and predictive modeling.
Now, you might wonder: how do we obtain the data regarding brain patterns? There are two primary methods: invasive and non-invasive. This article will focus on non-invasive techniques, which include neuroimaging methods like fMRI and EEG. Although these techniques are advantageous due to their non-invasive nature—eliminating the need for surgical procedures—they come with the drawback of lower resolution compared to invasive approaches.
Stay tuned for the continuation of this exploration!
Section 1.1: The Science Behind Mind Reading
To better understand mind reading, it’s helpful to consider some practical demonstrations of brain decoding.
The first video, "5 Simple Ways to Read Anyone's Mind | Revealed," showcases various techniques used in mind reading. It offers a fascinating perspective on how one might interpret thoughts through observation and inference.
Section 1.2: Practical Applications
Another engaging aspect of mind reading involves magic tricks and illusions that simulate the experience of mind reading.
In the video titled "I Am Going to Read Your Mind - Magic Trick," viewers witness how mentalism can create the illusion of reading thoughts, highlighting the interplay between perception and reality.